The cryptocurrency ecosystem is vast, with thousands of digital assets available today. However, not all cryptocurrencies are the same—some are coins, while others are tokens. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they represent fundamentally different concepts in blockchain technology.
This comprehensive guide will break down the key differences between coins and tokens, explore their use cases, and provide real-world examples to help you understand their roles in the crypto space.
What is a Coin?
A coin is a cryptocurrency that operates on its own independent blockchain. It functions primarily as digital money, similar to traditional currencies like the US Dollar or Euro, but with decentralized control.
Characteristics
- Native to its blockchain (e.g., Bitcoin runs on the Bitcoin blockchain).
- Used for payments, staking, or transaction fees within its network.
- Mined or staked (depending on consensus mechanism).
Examples of Coins
- Bitcoin (BTC) – The first cryptocurrency, designed as peer-to-peer electronic cash.
- Ethereum (ETH) – Powers smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps).
- Litecoin (LTC) – A faster, lighter version of Bitcoin.
- Monero (XMR) – A privacy-focused coin with untraceable transactions.
What is a Token?
A token is a digital asset built on top of an existing blockchain. Unlike coins, tokens do not have their own blockchain but instead rely on smart contracts (e.g., Ethereum’s ERC-20 standard).
Characteristics
- Created via smart contracts (no mining required).
- Represents assets, utilities, or governance rights.
- Highly customizable (used in DeFi, NFTs, and DAOs).
Examples of Tokens
- Chainlink (LINK) – Powers decentralized oracle networks.
- Uniswap (UNI) – A governance token for the Uniswap DEX.
- Tether (USDT) – A stablecoin pegged to the US dollar.
- Bored Ape Yacht Club (BAYC) – An NFT collection on Ethereum.
Key Differences Between Coins and Tokens
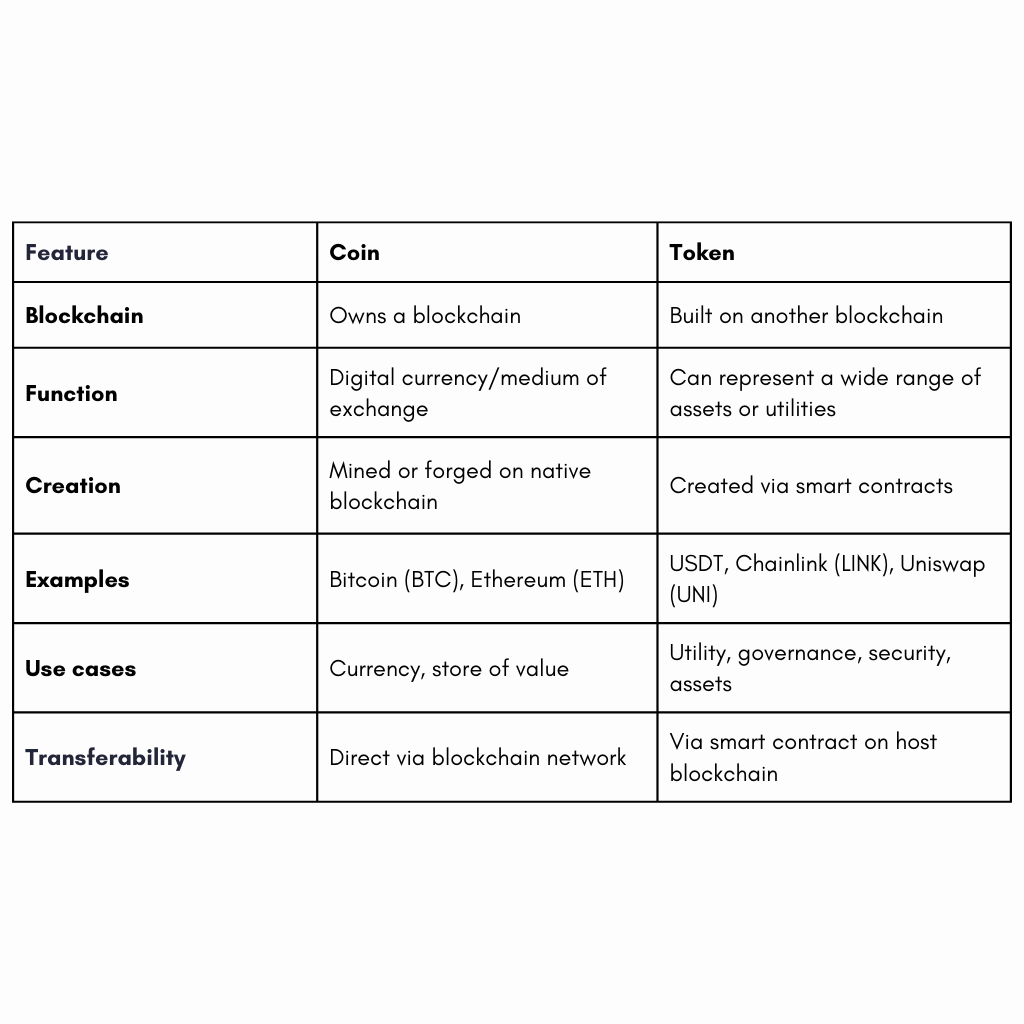
Why Does the Distinction Matter?
- Investment Perspective: Coins are primarily investments in the blockchain itself, while tokens often represent stakes in projects or products.
- Technical Development: Developing a coin requires creating and maintaining a new blockchain, whereas tokens are easier to create on existing platforms.
- Use Cases Impact: Tokens allow for complex ecosystems to be built on existing blockchains, enabling new models for governance, financing, and utility.
How Coins and Tokens Work Together
Many blockchain ecosystems involve both coins and tokens:
- Ethereum as a platform: ETH is the native coin used for gas fees, while tokens like DAI or BAT serve various purposes.
- DeFi applications: Use native tokens for governance but rely on coins for liquidity and transactions.
Risks and Challenges
Coins: Potential for blockchain forks, scalability issues.
Tokens: Depend on the underlying blockchain’s security and may be vulnerable to smart contract bugs or regulatory issues.
Conclusion:
Understanding the difference between coins and tokens is crucial for navigating the crypto space. While coins like Bitcoin and Ethereum serve as foundational currencies, tokens enable innovation in DeFi, NFTs, and governance.
Both have unique strengths—whether you’re an investor, developer, or enthusiast, knowing how they work will help you make better decisions in the evolving world of blockchain technology.
What’s your favorite coin or token? Let us know in the comments!




